A brief history:
For centuries people have made creative use of artifacts with the aim of ensuring authenticity (assurance that the product is original) and integrity (assurance that the product has not been altered from its original condition). To meet these demands, several solutions were created, such as wax stamping of royal seals to seal the king's correspondence, manual signatures on documents, watermarks on paper money, high-relief printing, special inks visible under black light, stamps holographic devices and a host of other technological resources.






On the other hand, there is a cat-and-mouse race between the anti-counterfeiting market on the one hand and counterfeiters on the other, the former creating and developing innovations in the sector while the latter capitalizes on and accompanies the former. Thus, more and more resources and technology were invested in the search for new solutions, making the physical shield, the target of protection, increasingly expensive and complex.
A paradigm shift
Why not change the focus of the application of the technological barrier, migrating it from the physical object to a digital object, this allows scale, security and customizations in real time. In order to respond to this new paradigm, we have developed a technology that provides the final customer with clear information about the authenticity of the object he has acquired on the market.
For the entrepreneur, it would be something similar to providing a different certificate of originality for each of his manufactured items, so that the final customer can check the authenticity of this item using his cell phone by simply reading a QR code. This object is then tracked and linked to its manufacturer.
This is a technology innovative and disruptive, as it extracts the security barrier from a physical object to the virtual environment, storing it securely in the cloud. It is quite common to hear news about the counterfeiting of money, however until today I have not seen any news about the counterfeiting of bitcoins.
Would it be possible to fake bitcoins?
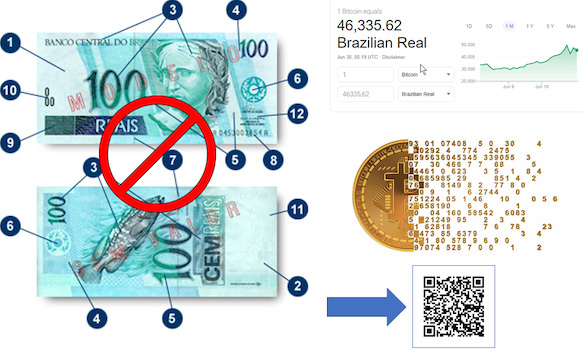
The development of cloud technologies brought support for a paradigm shift so that security features previously coupled to the physical object migrated to a set of algorithms protected by a WEB server. Thus, a single QR code can provide superior protection to physical artifacts, making product counterfeiting an unfeasible activity.
2QR Secure Technology (Anti-Piracy)
Our solution is based on a card / sticker containing 2 QR codes so that the reading of the first informs the description of the object and its traceability, while the reading of the second QR code provides the authenticity of the object.

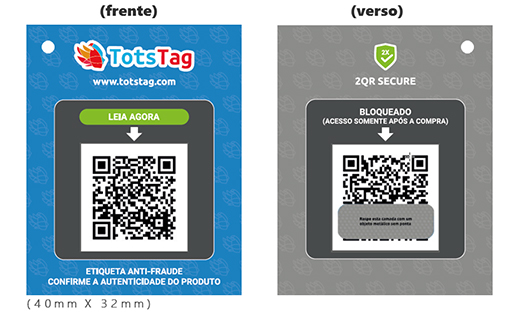

How it works?
2QR Secure Technology makes use of secure and unique keys in order to guarantee the identity of each item, something similar to the CPF number, but in this context it allows the identification and monitoring of each item, taking into account issues of authenticity and physical movement.
To facilitate understanding, let's make an analogy to an identity document. To validate a citizen's identity document, it is necessary to apply some security concepts to a paper ballot used to make this document:
Physical barriers to inhibit counterfeiting: Information about a citizen's identity is printed on paper money containing layers of special features such as watermark, auto-relief, special inks that glow under blue light, holographic markings and other features that aim to inhibit counterfeiting. of the physical screen that receives the information – the identity card.
Unique code: Here we have the application of a unique code that distinguishes one banknote from another, something similar to the serial number of an item. This type of number/code is already quite common, for example, we can mention the CPF number, where each citizen has a different CPF and all information related to the citizen will be linked to this number.
Biometric data: At this point we already have a paper currency that inhibits the falsification of the physical screen, we have a code that distinguishes each citizen and finally we need to link this identity to the citizen's biometric data, in order to seal the physical link between the citizen and the identity document. Here comes the pen signature and fingerprints that accumulate evidence to the identity link.
Legitimacy of issuance: To give legitimacy to this information, there is a need for standardization of procedures, custody of information and people trained to analyze cases of suspected fraud. Thus, there is a need for an entity responsible for processing, managing and supervising these processes.
That's it, this is the basic concept of identity for the most diverse applications from the issuance of identity cards, passports, driving permits, digital certificates and employee badges. We can observe a variation of the applied technology, however the conceptual aspect remains valid.
Now, we are going to bring these aspects to the TotsTag platform and demonstrate how the concept of identity can be effectively applied to products of the most varied types.
In place of physical barriers to inhibit counterfeiting: On the TotsTag platform, the physical shield, paper money, becomes unnecessary, this because a simple QR code directs to a digital profile located in the cloud and which cannot be changed. Something as if the paper money were in the cloud and could only be viewed by most people, however its edition follows predictable processes and is easily audited.
In compliance with the unique code: Each product/object receives a unique code similar to a CPF that distinguishes it from the others and so for a box of medicines containing 10 ampoules of medicine, each ampoule would have a different code (CPF).
In response to biometric data: How to collect biometric data from objects such as medicine boxes, guitars, bicycles, electronics and a host of other products? Here's another challenge. Biometric data is evidence that creates a physical bond of identity.
During the useful life of any product, from its manufacture to its disposal, it relates to people and thus creates a story guided by its timeline. For example, when a father goes to a store and buys a bicycle to give as a gift to his son, that bicycle is at the beginning of his historical timeline that goes from its manufacture (birth) to its disposal (death) in a time future, at this moment we are at a point in this timeline where the bicycle has passed through different profiles (legal entities and individuals) from the factory, distribution center, wholesaler, retailer and now to the hands of the father who is going to gift his son . Thus, the history of bicycle movement by each of these “players” provides evidence of the identity that makes up part of the term “biometric data” discussed at this point.
Biometric data is evidence that can be reinforced by more evidence, so in addition to the signature on a paper ballot, in the previous case, the fingerprint is also used.
The next evidence will be definitive to give consistency to the authenticity aspect of the item.
Imagine a 48-position alphanumeric key something like this (sWu11sTHUxpIPwC0z5wWK7xqf7XQZoEadGWGX0zNXJ6qY72u) to get an idea of the complexity of this key, it is easier to hit 7 times in a row on LOTTERY than hitting these combinations of letters and numbers, that is, a non-predictive key (cannot be guessed).
Now when this key is hidden on a card next to the object and covered by a scratch-off, the first person who has access to this key will be able to consult it on the WEB server and thus obtain a positive authenticity and cancel the key on the server after the first read.
Here comes the “cat jump” all the previous points would fall apart if a counterfeiter copied the QR code and replicated it to other counterfeit items simulating the identity.
However, imagine that now a counterfeiter does this, scratches the scratch-off, gets access to the code, does not read it and copies the code for 5000 counterfeit items and in each of these objects he covers with the scratch-off to simulate not violated .
In this case, when the first client reads the code, it will be positive for authenticity and this key will be released from the server. What will happen to the other 4999 items? This will even answer negative for authenticity.
So in the best case the forgery will occur in a ratio of 1 to 1, something like taking the seal off an original object and sticking the seal on a fake object.
This makes the counterfeiting process financially unfeasible, it is not worth counterfeiting 1 to 1, but counterfeiting in the proportion of 1 to 5000, 1 to 10000, 1 to 100000 if not more.
In compliance with the legitimacy of issuance: Each person (individual or legal entity) has a profile in the system and thus he will assume roles when issuing these seals and will be part of the traceability process that identifies the movement of the product, with this digital profile the requirement of legitimacy for the issuance is fulfilled. of the seal and participation of the registered distribution chain in the traceability process.

This type of Tag is resistant to cloning (copying the tag) so that if it were copied the first reading would render all other cloned tags useless.

2QR Secure Technology links the registered object to a social footprint (traceability) so that the new customer can still be part of this supply chain by taking digital ownership of the item.

Because 2QR Secure is cloud-based in nature, it supports a set of features and makes it possible to manage each item in real time.
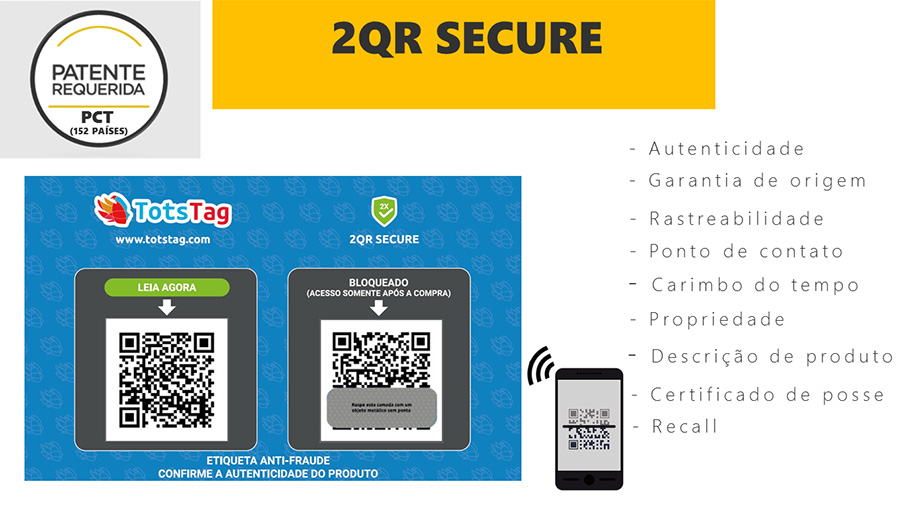
Simplicity of use for the end customer
This technology is very friendly to the end customer as it offers the following facilities:
- No need to download app.
- To read the label, just have a cell phone connected to the internet with a QR code reading feature.
- The information obtained from the reading is clear without the need for interpretation by a professional.
The end customer will scan the free QR code (not blocked by the scratch card) and will then have access to the traceability of the object, identifying descriptive data of the product and its manufacturer.
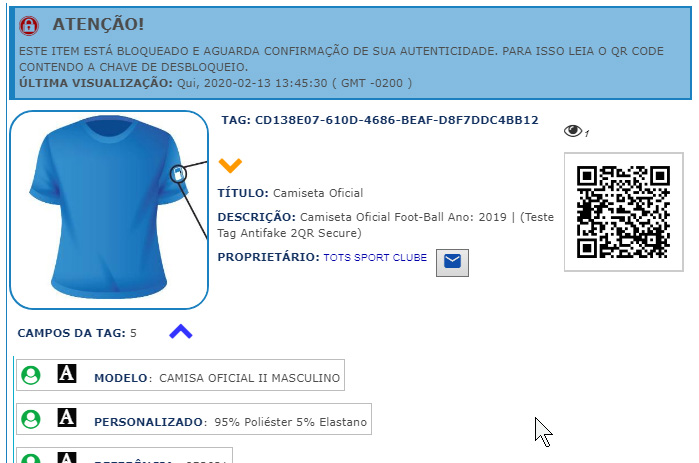
After purchasing the item, the customer scratches the partially covered QR code and confirms the authenticity of the object.

Any new reading for this object will inform you that it was already unlocked in a previous time and that this object is not safe.

Access the QR code below and see more information about this example Tag.

Value Assessment Matrix (2QR Secure X Holographic Labels)
This value matrix compares the effectiveness of 2QR Secure technology against the use of holographic seals. Holographic seals are used to inhibit counterfeiting processes because they offer barriers to replication difficulties in view of the need for high-value optical equipment, thus limiting the barrier to entry.
On the other hand, technology evolves very fast and these equipments become increasingly accessible and enter the cost/benefit curve of counterfeiters. Even if the holographic seal forgery is of poor quality, the person performing the validation is usually the end customer who lacks the expertise to assess the authenticity of the holographic seal. Some copies are still of such quality that even technicians have to send samples of the suspected product for confirmation via laboratory analysis.
Another layer of technology used with holographic seals is an individualized numbering per seal or per batch in order to be confronted in the future with a database to facilitate the confirmation of authenticity, even this resource still fails to provide the end customer with tools authenticity audit as this numbering normally serves internal systems and can still be easily replicated.


Legend:
- Authenticity confirmation (company): This is related to the ability to audit a label as to how to confirm its authenticity by members of the company. Here, an interesting point is that the more technological resources are applied to the physical screen, the greater the need for specialized tools and time to validate authenticity in an audit process, this point also affects the numbered holographic label.
- Authenticity confirmation (end customer): This is related to the ability to audit a label as to confirm its authenticity directly by the end customer. When we take into account the company's agents, this aspect becomes less hostile because it has specialists to carry out this audit process, since when it comes to the final customer, this one lacks the means for evaluation, so a falsification of the physical screen would imply in difficulty for evaluation with the end customer.
- Product Identification: Ability to identify and qualify the product to which it refers.
- Traceability: The end customer can perform a complete traceability of the item by simply reading the QR code on the label.
- Contact point: The end customer can choose to be part of the supply chain, taking digital ownership of the Tag, thus creating a digital link between the object, the end customer and the manufacturer that can now be used as a two-way communication channel.
- Lead Routing: When the customer reads the Tag and confirms its authenticity, he can now interact with a call like: – Would you like to join our diamond club and compete for incredible prizes – click here – This way the customer would be directed to the product manufacturer's page.
- Recall: If something goes wrong after distributing its product, the manufacturer can use the Recall feature to provide a message to customers who read the label, in order to refine the company's product recall process.
Note:
1) – The ranked values in the table range from 0 to 5.
2) – In the value matrix chart, due to not being possible to validate a grade for the item Authenticity confirmation (end customer) it was given 50% of the score value , this taking into account the unavailability of data to assess the counterfeit quality of a holographic seal as well as evaluating the end-customer's expertise to identify a counterfeit holographic seal.

